Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry, providing a reliable and long-lasting solution for tooth loss. However, like any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with dental implant placement. It is important to be aware of these risks and take necessary precautions to minimize them. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the potential risks and diseases related to dental implants, and explore ways to mitigate them.
Understanding Dental Implants
Before we delve into the risks and diseases associated with dental implants, let’s first understand what they are. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots made of titanium that are surgically placed into the jawbone. These implants serve as a foundation for replacement teeth, such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. They provide stability and support for the prosthetic teeth, allowing for improved chewing ability, speech, and aesthetics.
The Success and Safety of Dental Implants
Dental implants have an impressive success rate, with studies showing a success rate of 95-98% when placed by experienced dental professionals. This means that the majority of patients who receive dental implants experience no complications and enjoy the benefits of restored oral function and aesthetics. However, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks and complications that can arise.
Risks Associated with Dental Implant Procedures
1. Infection
Infection is a significant risk associated with dental implantation. Bacterial plaque accumulation around the implant can lead to infections, causing abscesses, inflammation, and suppuration. In some cases, the infection can spread to other areas of the body, causing systemic infections. While prophylactic antibiotics are often administered before the implantation procedure to reduce the risk of infection, they may not completely eliminate the possibility. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can help prevent and detect infections early.
2. Failure of Osseointegration
Osseointegration refers to the process of the dental implant fusing with the jawbone. It is a critical step for the long-term success of the implant. However, there is a risk of failure in achieving proper osseointegration. This can occur due to various factors such as inadequate primary stability of the implant, poor bone quality, or improper surgical technique. If osseointegration fails, the implant may become loose or fail to integrate with the jawbone, necessitating removal or replacement.
3. Nerve Damage
During the implantation procedure, there is a potential risk of nerve damage in the surrounding tissues, such as the teeth, gums, lips, or chin. This can result in pain, numbness, or paresthesia in the affected areas. It is crucial for the dental professional to have a thorough understanding of the anatomy and take necessary precautions to minimize the risk of nerve damage during the procedure.
4. Perforation of Anatomic Structures
In some cases, the placement of dental implants may result in the inadvertent injury or perforation of nearby anatomic structures. This can include perforation of the maxillary sinus, inferior border, lingual plate, labial plate, inferior alveolar canal, or gingiva. For instance, perforation of the maxillary sinus can lead to sinus problems and infections. Proper planning, imaging techniques, and experienced practitioners can help minimize the risk of perforation.
5. Excessive Bone Loss
Excessive bone loss around the dental implant can compromise the stability and success of the implant. It can occur due to various factors, including poor oral hygiene, peri-implantitis (inflammation around the implant), and natural bone resorption. Excessive bone loss may require additional interventions, such as bone grafting, to restore the stability and aesthetics of the implant.
6. Complications with Prosthetic Teeth
The artificial teeth attached to the dental implants can also pose certain risks and complications. Cement used to secure implant-supported teeth can sometimes lead to inflammation and peri-implant disease if not properly cleaned. Additionally, mechanical complications, such as abutment screw breakage or fracture, can occur. These complications may require repair or replacement of the prosthetic teeth.
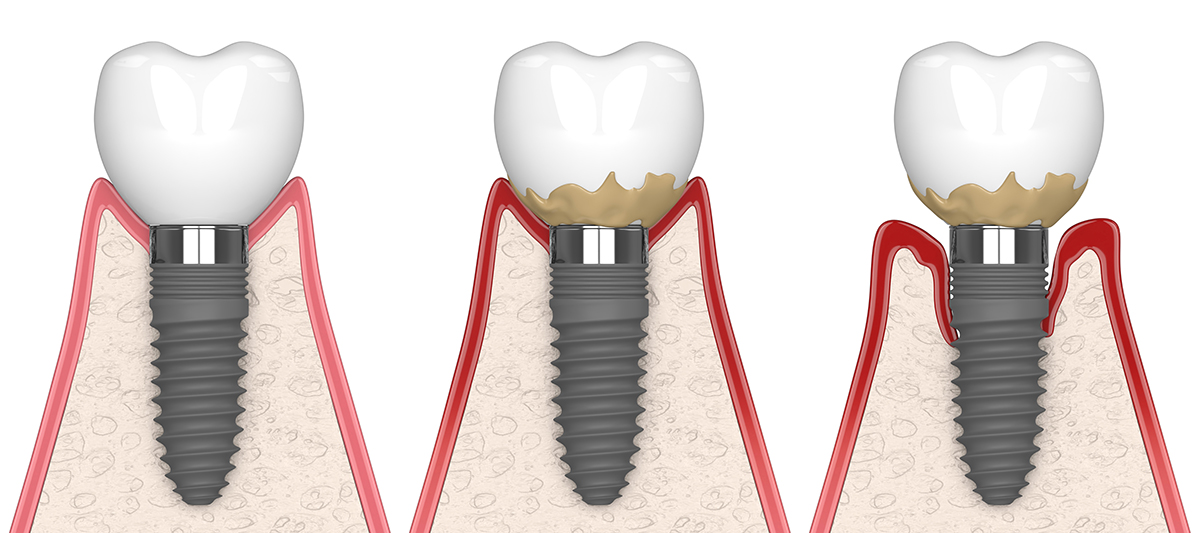
Peri-Implant Diseases
Apart from the risks associated with the implantation procedure itself, there are specific diseases that can affect the soft and hard tissues surrounding dental implants. These conditions are referred to as peri-implant diseases and can lead to complications if left untreated.
1. Peri-Implant Mucositis
Peri-implant mucositis is an inflammatory condition that affects the gum tissue around the implant. It is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding upon probing. If detected early, peri-implant mucositis can be treated non-surgically by thorough cleaning and improved oral hygiene practices. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are crucial for the early detection and management of peri-implant mucositis.
2. Peri-Implantitis
Peri-implantitis is a more severe form of peri-implant disease characterized by inflammation of the gum tissue and bone loss around the implant. It is often caused by untreated peri-implant mucositis and can lead to implant failure if not addressed promptly. Treatment of peri-implantitis may involve surgical interventions such as implant detoxification, bone grafting, and antimicrobial therapy.
Factors Affecting Dental Implant Complications
Several factors can influence the risk of complications associated with dental implants. It is important to consider these factors before undergoing the implantation procedure to determine the likelihood of success and minimize the risks.
1. Oral Health
Maintaining good oral health is crucial for the success of dental implants. Untreated tooth decay, active periodontal disease, and poor oral hygiene can increase the risk of infection and implant failure. It is essential to address any existing oral health issues before proceeding with dental implant placement.
2. General Health
General health conditions can also impact the success of dental implants. Conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes or diminished jawbone strength and thickness can compromise the integration of the implant with the jawbone. It is important to discuss any underlying health conditions with your dental professional to assess the suitability of dental implant treatment.
3. Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for implant failure and complications. Tobacco use can impair blood flow and compromise the healing process, leading to an increased risk of infection, poor osseointegration, and gum disease. Quitting smoking before undergoing dental implant placement can significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome.
Minimizing Risks and Ensuring Success
While there are inherent risks associated with dental implant procedures, there are steps you can take to minimize these risks and increase the likelihood of a successful outcome.
1. Choose a Skilled and Experienced Dental Professional
Selecting a skilled and experienced dental professional is crucial for the success of dental implant treatment. A qualified implant surgeon can accurately assess your oral health, plan the implant placement procedure, and minimize the risk of complications. Take the time to research and choose a reputable professional with a track record of successful implant placements.
2. Follow Proper Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential for the long-term success of dental implants. Brushing your teeth twice daily, flossing regularly, and using antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent plaque accumulation and reduce the risk of peri-implant diseases. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also essential for monitoring the health of your implants and addressing any potential issues promptly.
3. Follow Aftercare Instructions
Proper aftercare is crucial for the healing and integration of dental implants. Your dental professional will provide specific instructions on post-operative care and hygiene practices. It is essential to follow these instructions diligently to minimize the risk of infection, promote healing, and ensure the long-term success of your dental implants.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Leading a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to the success of dental implants. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight can promote overall oral and general health. Additionally, managing chronic health conditions such as diabetes can help reduce the risk of complications.
5. Attend Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for the early detection of any potential complications or issues with your dental implants. Your dental professional will assess the health of your implants, perform necessary cleanings, and address any concerns. Prompt intervention can help prevent the progression of peri-implant diseases and ensure the long-term success of your dental implants.
In conclusion, dental implants are an excellent solution for replacing missing teeth and restoring oral function and aesthetics. While there are risks associated with dental implant procedures, proper planning, skilled professionals, and diligent aftercare can minimize these risks and increase the chances of a successful outcome. By understanding the potential risks, following proper oral hygiene practices, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can enjoy the benefits of dental implants for years to come. Remember to consult with your dental professional to assess your individual risk factors and determine the best treatment plan for your dental implant needs.